What is IoT?
IoT stands for the Internet of Things. It is a network of physical objects that connect to the Internet to exchange data between other connected devices (Machine to Machine), or IoT systems in order to provide a range of services and functionality from monitoring how full bins are for refuse collection to monitoring your heart rate on a smart phone, the range of possibilities for IoT Technology is huge with predictions that global IoT revenue will reach $600 billion by 2030 with over 29 billion devices connected.
Multi Network IoT Sim Cards
Connect to multiple UK and Worldwide Mobile Networks operators from one Sim card.
What are the use cases and examples of IoT?
In this blog we will discuss several current real-world use cases for IoT Technology such as the Smart Home and Automotive, but these use cases are only scratching the surface on the potential for IoT applications. As the development of AI (Artificial Intelligence) system emerge along with new 5G networks the IoT space is extremely exciting.
The Smart Home
IoT within the home and home automation systems is one area that is well established and one area that we all have the most experience already with an array of smart devices available. One of the main IoT technologies we use is Amazon Alexa and Google’s SIRI that provide virtual assistant technology to help us with shopping or reminding us of tasks and answering questions.
Other smart home technologies help us with reducing our energy bills and carbon footprint with the use of smart meters and smart thermostats that can turn our heating off when we are not at home, or automatically change the heating dependent on the outside ambient temperature, or in-conjunction with a movement sensor can just heat rooms with people in.
Home security systems and smart doorbells help protect our homes providing us with the ability to answer the door from the other side of the world or alerting us to unwanted intruders.
Other areas we may not realise are already in place or being developed in the home are IoT sensors within our boilers and other home appliances that can send diagnostic information to the manufacturer to warn them of a heating element failure or that your boiler needs a service as part of the Warranty purchased with the appliance. The benefit to the manufacturer is they can save costs with pre-emptive replacement of potentially faulty parts or ensuring your service plan is up to date with scheduled reminders.
The smart home ecosystem and home automation is here to stay, so watch this space!
Automotive
If you have purchased a new car over the past 5 years it is highly likely that your Car’s computer system will have some form of connectivity to the Internet, GPS, and Satellite Navigation.
The connected car in conjunction with an IoT application / smart phone app allows a user to view a cars location, change climate controls, lock doors, and check the status of the car.
Car manufacturers use the connected car to check on a car’s components and service status. With the progress in self driving cars, artificial intelligence, and automation we already have cars that can drive themselves without human intervention. Looking into the future with small cell 5g deployments it’s possible that all the cars on a motorway could be centrally controlled to improve traffic flow with real time communication between each car on the road network.
Smart Cities

Cities and local councils are deploying IoT technology to improve efficiency, sustainability and improve the quality of life of city residents.
Smart Energy management systems monitor and optimize energy use across the public infrastructure of a city covering buildings and street lighting adjusting usage dependant on the time of day or how busy a street or building is.
Intelligent transportation and environmental monitoring can improve traffic flow across a city’s road network reducing pollution levels.
Smart IoT waste management systems can track how full bins are to optimize waste collection services and improve recycling.
Monitoring of water systems and waste management can test water quality, detect leaks in pipes and optimise water usage in parks to improve sustainability and cut waste.
These are just a few examples of IoT in smart cities. The potential applications are vast, and as technology continues to advance, new use cases will emerge, making cities more efficient, and sustainable..
Healthcare
IoT solutions within the Healthcare sector are already firmly established with most of us having experienced wearing a smart watch or other wearables that can monitor our heart rate, body fat, stress levels and more. Apple now claim their smart watches can spot if you are having a heart attack and alert the emergency services to your geo location.
Other applications for IoT in healthcare include the ability to track patients during their stay in hospital, track expensive assets and drugs to ensure stock levels are correct and items not missing. Monitoring patients from home allowing for earlier discharge and better recovery outcomes for the patient.
As IoT technology continues to develop the advantages of using IoT in Healthcare has a huge range of benefits from costs savings to patient recovery times.
Industrial IoT
Industrial IoT refers to the application of IoT technologies in industrial settings including manufacturing, logistics, energy, and agriculture. Industrial IoT improves industrial processes, delivering increased efficiency, productivity, and insights to production cycles. Here are some key use cases of Industrial IoT:
Supply Chain IoT in-conjunction with blockchain technology delivers end-to-end visibility and traceability of goods in real-time, monitoring storage conditions and improving efficiency.
Quality control systems are using sensors to monitor production processes, collecting data on a products quality, and reducing defects which in turn reduces waster and delivers a consistent product.
Predictive maintenance IoT can analyse and monitor a range of machinery, equipment and infrastructure collecting information from sensors to monitor vibration, temperature, and other parameters. The data collected can warn of a potential failure in the equipment improving the lifetime of equipment and reducing costs.
These are just some of the potential transformative use cases of Industrial IoT in improving industrial operations, reducing costs, and improving safety.
Register for a free 30 day IoT SIM Card Trial
Our trial IoT SIM cards provide 500Mb of data and 30 sms messages, connecting you to EE, Vodafone and O2 networks for test IoT projects.
What was the first IoT device?
It is difficult to pinpoint what the first IoT device was, one could argue that the advent of smart phones were the first true IoT devices however, in 1982 researchers from Carnegie University connected a Coke machine to the early Internet with a range of sensors to monitor stock levels and the temperature of drinks.
What is an IoT Platform?
An IoT platform is a centralised software infrastructure that provides management of IoT devices and data. It serves as a foundation for building, deploying, sharing data, and managing IoT applications and services.
An IoT platform typically provides several key functionalities:
IoT Device Management
Allows for the onboarding, provisioning, and configuration of IoT devices and sensors. This includes tasks such as device registration, software updates, and monitoring device health.
Connectivity
An IoT platform provides and facilitates communication between IoT devices and other components of the IoT ecosystem, such as IoT gateways, cloud services, and applications. An IoT platform supports secure communication protocols and standards to ensure end-to-end security of systems and devices.
Data Management
An IoT platform can collect data, and process data generated by IoT devices. It can provide machine learning, data analytics and visualization of IoT data. Data management features often include data filtering, transformation, and aggregation.
Application Enablement and Integration
IoT platforms provide tools and APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) for developers to build IoT applications and services. These tools often include software development kits (SDKs), APIs for data access, blockchain technology and device control, and frameworks for building IoT solutions. An IoT platform enables the integration of IoT data with other systems such as databases and ERP systems allowing for seamless exchange of data.
IoT platforms are used in various domains, including smart cities, industrial automation, agriculture, healthcare, and transportation. They play a crucial role in managing the complexity of large-scale IoT deployments, enabling organizations to collect, analyse, optimize, and derive insights from the big data generated by connected devices.
Both Amazon (AWS IoT) and Microsoft (Azure IoT) are providers of IoT platforms operated from their Cloud Computing platforms.
Stream Networks IoT platform Cascade provides management and monitoring of IoT sims and connectivity. Contact our IoT team on 01635 884170 to find out how Cascade can help with your IoT deployment.
What Internet connectivity is used in an IoT Network?

All types of Internet Connectivity can be used in an IoT Network from fixed line wired ethernet, broadband, WiFi networks, Bluetooth connectivity between a sensor and gateway and more commonly IoT mobile sim cards and low-power Wide Area Network technology.
The most common form of IoT connectivity are IoT sim cards that connect a sensor or IoT device to a mobile phone network. IoT sim cards are very cost effective as he data requirements in IoT projects are normally small, so it is possible to connect IoT devices for less than £0.50 per sim.
Read about IoT and multi network SIM’s here.
What is NB IoT?
Narrowband Internet of Things is a Low Power Wide Area Network (LPWAN) technology specifically designed for the Internet of Things (IoT). It is a cellular-based wireless communication standard that enables efficient, low-power, and long-range connectivity for IoT devices.
Narrowband technology is designed for low power consumption allowing for sensors to operate on battery or small cell solar panels for extended periods of time.
The advantages of low-power technology are that it provides an IoT connectivity for solution for devices in remote locations that have no access to power such as bins, temperature sensors monitoring railway tracks, asset tracking, environmental monitoring, agriculture, and industrial automation.
Narrowband operates within licensed spectrum bandwidth, leveraging existing cellular infrastructure and benefiting from the wide availability of cellular networks globally.
What is Cat-M1?
Cat-M1, also known as LTE-M1 or LTE Cat-M1, stands for Category M1. It is a Low Power Wide Area Network technology designed for IoT and machine-to-machine (M2M) communication over existing cellular networks. Cat-M1 is a subset of the Long-Term Evolution (LTE) cellular standard and operates in licensed spectrum bands.
Stream Networks provide a range of SIM cards that provide Cat-M1 connectivity for IoT deployments please contact sales on 01635 884170 to find out further information.
What is an IoT Gateway?
An IoT gateway is a hardware or software component that serves as an intermediary between IoT devices and the cloud or central IoT infrastructure. It acts as a bridge, connecting the local IoT network or devices to the wider network or internet. IoT gateways can be found in LowPower Narrowband networks to provide connectivity from the sensors to the Internet.
What is an RFID tag?
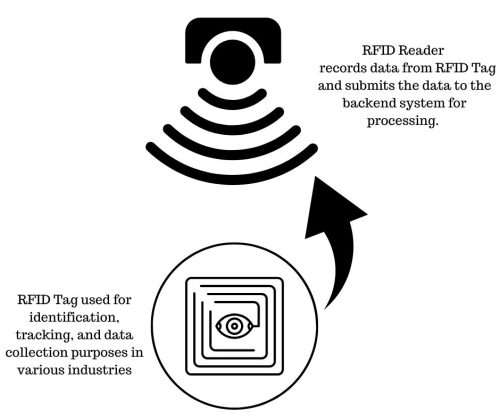
An RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) tag is a small electronic device that consists of a microchip and an antenna. Used in-conjunction with an RFID reader and a backend system to process data RFID tags are used for identification, tracking, and data collection purposes in various industries.
The RFID tag contains a unique ID and other data related to the product on the RFID ‘s microchip. When passed by a reader the reader records the data and submits the data to the backend system for processing.
RFID tags are commonly used in tracking of assets in Healthcare, Manufacturing, and industrial processes.
What is remote monitoring IoT?
Remote monitoring IoT refers to the use of Internet of Things technology to monitor and collect data from devices, systems, or environments remotely. It enables real-time data acquisition, analysis, and control of connected devices or sensors through a cloud-based platform. Remote monitoring IoT has numerous applications across industries, offering benefits such as improved efficiency, reduced costs, and enhanced decision-making.
What type of sensors are used in IoT?
IoT deployments use a wide range of sensors to collect data from the physical world and enable the monitoring and control of various processes. The choice of sensors depends on the specific IoT application and the type of data that needs to be captured. Some of the commonly used sensors in IoT are:
Temperature Sensors measure ambient temperature and are used in supply chain to monitor the temperature of goods in transit, environmental monitoring, and monitoring of industrial processes.
Humidity Sensors measure the moisture content in the air and are often found in weather monitoring and agriculture.
Motion Sensors detect movement or changes in position of a device or object. Motion sensors are used in wearable devices, security systems, and asset tracking.
Gas sensors detect the presence and concentration of gasses in the environment. Used in Smart Cities, and Industrial deployments to track pollution levels.
Sound Sensors – Sound sensors capture and measure sound waves. Typically, sound sensors are found in voice recognition systems and noise monitoring.
GPS Sensors determine the exact location of devices and are used in asset tracking and fleet management.
Proximity sensors detect the presence or absence of an object within a certain range used in smart lighting, industrial automation, asset tracking and security systems. See also RFID Tags
What is IoT Security?
As IoT technology develops consideration needs to be given to cybersecurity systems and security issues as failure in an IoT system can be serious.
IoT security is a complex fields and consideration needs to be given to vulnerabilities across your IoT deployment. Device authentication, data encryption, firmware updates, access control (zero trust networks) and ensuring your IoT estate has regular penetration testing and auditing is key.
With the sheer potential of numbers of devices being able to connect to the Internet (23 billion devices by 2025) we may see more IoT projects utilise the new larger IPv6 internet address space over IPv4 which has limited amount of IP addresses available. IPv6 has advanced built in IPsec security features built in to IPv6 extension header providing enhancements in packet authentication and data integrity.
Stream Networks are also working with partners in the field of Quantum security to ensure network deployments are future proofed against Quantum computing encryption hacking.
What are the overall benefits of IoT?
IoT has many benefits across all sectors of industry supporting new business models, improving ROI and decision making.
It’s important to note that while IoT offers lots of benefits, there are also challenges related to security, and scalability that need to be addressed. With proper planning, implementation, and governance, organisations can harness the potential of IoT to drive significant value and support digital transformation.
If your business is looking at IoT solutions to improve your business or customer experience, please contact our IoT team on 01635 884170 or complete the contact form below.

