This blog explores SD-WAN architecture and what is needed for a successful SDWAN deployment. SD-WAN (Software-defined wide area network) technology is now becoming the de facto and most cost-effective way to connect branch offices, remote workers, and data centre’s into a secure wide area network. This is due to several factors such as the growth in lower-cost fibre broadband connectivity and the increase in the use of cloud applications being consumed across the public Internet that make legacy wan technology such as MPLS (MultiProtocol Label Switching) and IPVPN’s inflexible for wan optimization, security, and application performance.
This blog helps uncover what you need to consider when deploying a software-defined WAN and the SD-WAN architecture required to ensure a successful SD-WAN deployment.
SD-WAN Architecture Overview
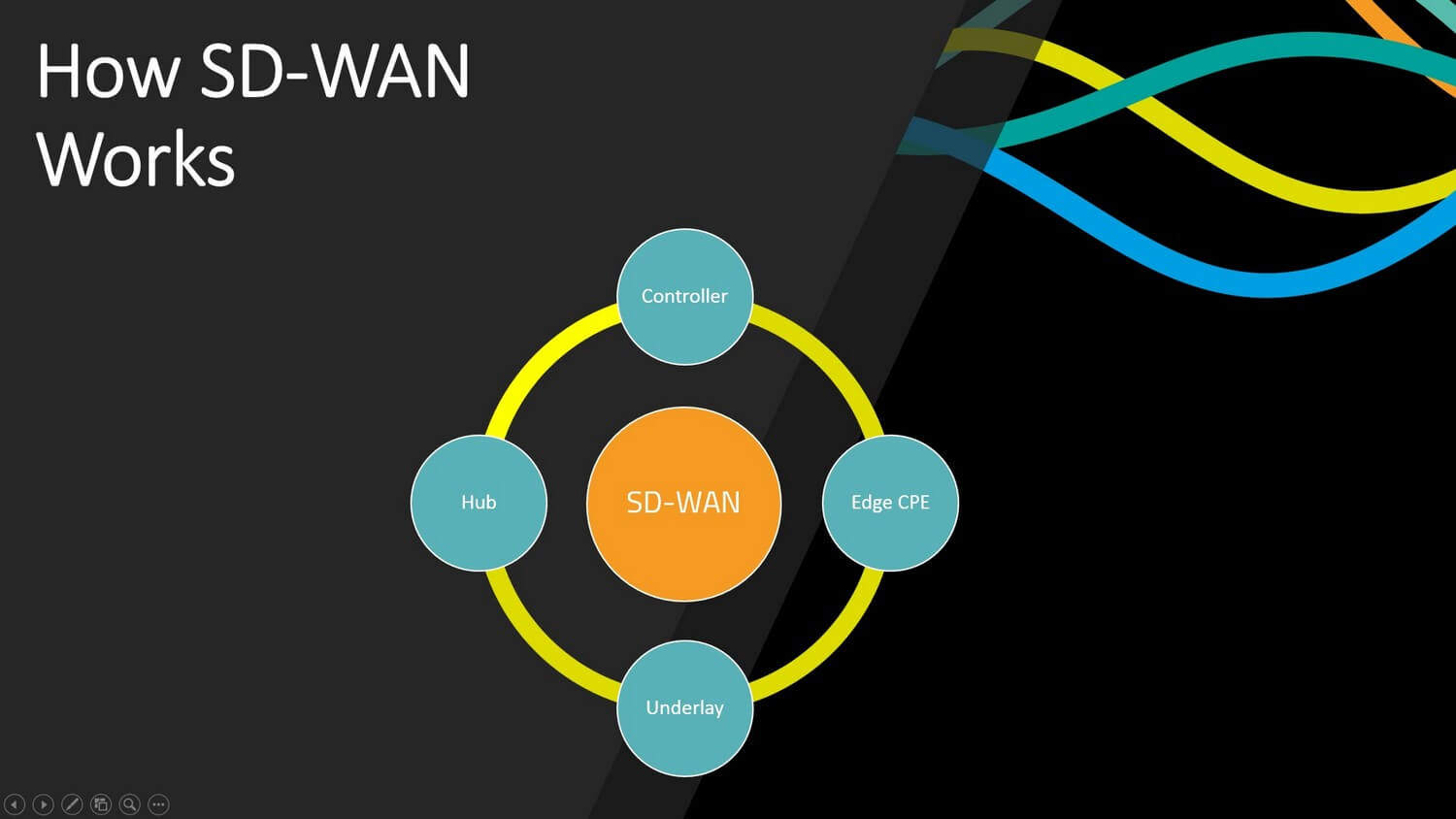
A software-defined wide area network has four key components or building blocks as follows:
- An Orchestration Platform
- An SD-WAN hub
- SD-WAN Edge / Endpoint devices
- Underlay connectivity
It is key when engaging with an SD-WAN service provider that you understand how they are proposing to build your SD-WAN network and what components their SD-WAN solution includes as some SD-WAN solutions don’t include all the components required for a successful implementation.
What is an SD-WAN Orchestrator?
An SD-WAN Orchestrator is a centralized management platform typically a web GUI that you log on to and which gives you secure control over your wide area network, and wan connectivity.
An SD-WAN Orchestrator allows you to manage your edge devices, create secure tunnels to other endpoints, delivers network automation, manages application traffic, creates load balancing rules, manages Virtual Network Functions (VNFS), allows you to view traffic flows and update security policies to all devices on your network. It is a single pane of glass for your entire network infrastructure.
Key points to consider with an SD-WAN Orchestration Platform
It is important that you evaluate the SD-WAN provider’s orchestration platform to ensure that the orchestrator fits your business and IT needs.
An SD-WAN orchestrator should be user friendly, allowing IT teams to easily access and gain insight into the network in real-time.
It should include the ability to monitor the health state of an edge device from memory consumption to CPU and the device operating system state.
It should provide easy device configuration through the implementation of ZTP (Zero Touch Provisioning) that allows for templated device configurations and operating system upgrades.
The orchestrator should include the ability to provide a graphical map overview of your entire network clearly pinpointing any issues with your device’s bandwidth consumption, underlay or software overlay elements.
It should provide the ability to monitor your networks routing, security and firewall event logs and highlight any potential security threats to your network.
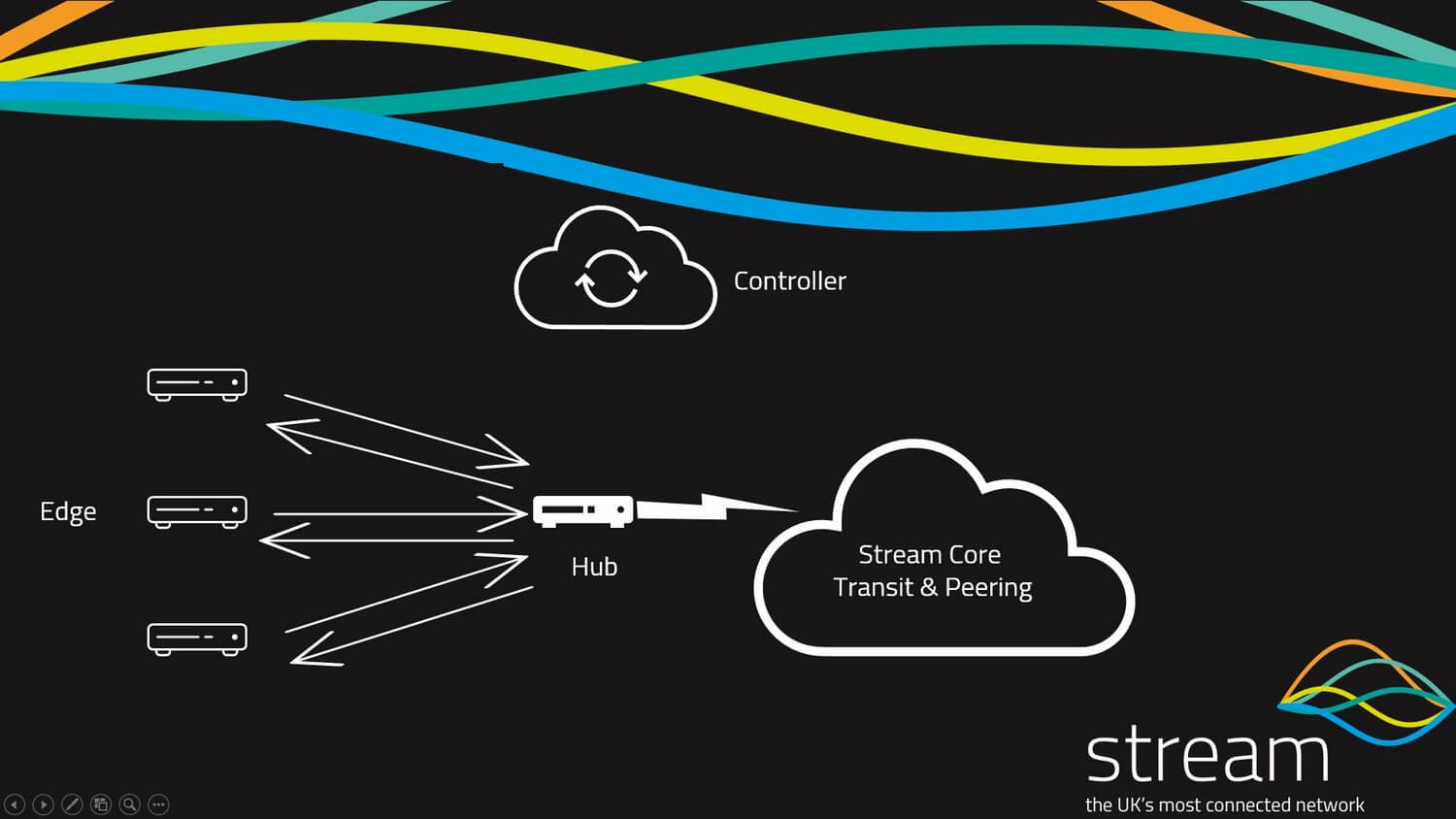
What is an SD-WAN Hub?
An SD-WAN Hub is a gateway for your endpoints to centrally connect to, to build a Hub and Spoke or fully meshed Wide Area Network. An SD-WAN Hub is a key element as it provides end to end application control and QoS (Quality of Service) for application traffic across the network.
Key points to consider with an SD-WAN Hub
Some SD-WAN service providers and sd-wan solutions do not include an SD-WAN hub within the network design. They rely on building point to point IPSEC VPN tunnels between edge devices. You should work with your provider to understand how the solution they are proposing delivers application steering and inter-site connectivity.
In a point-to-point scenario where no hub exists you are relying on each edge device to connect to another edge device making the network design more complex and from an application performance point of view it’s the edge device making decisions about the network traffic locally. An SD-WAN Hub delivers a better less complex network topology and delivers application monitoring from the core of the network, monitoring traffic flow at every site which delivers complete end to end application performance.
For example, if you are troubleshooting inter-site connectivity a hub and spoke network delivers a less complex network, If an underlay circuit at a data centre or HQ has an increase in latency, packet loss or jitter that affects Microsoft RDP traffic, with a non-hub design the data centre traffic will flow over an alternative path at the data centre, however, the other branch offices may not see the traffic flow change. With a hub design, it monitors application traffic from end to end.
One thing to consider though when building a hub and spoke SD-WAN design is to ensure you have Hub failover which can lead to an increase in deployment costs as you need to purchase two hubs. If you only have one hub what happens if you lose connectivity to the hub or experience a hardware failure? It is important that you deploy Hub failover technology, and you should talk to your provider to understand how failover is delivered.
Stream Networks provide SD-WAN hub disaster recovery within our managed service. Failover is achieved by using IPSEC HA with each hub located in geographically diverse data centres. Each customer network is built so every individual edge device has connectivity to a primary and secondary hub, should the primary hub fail, traffic is automatically routed to the secondary hub.
What is an SD-WAN Edge Device?
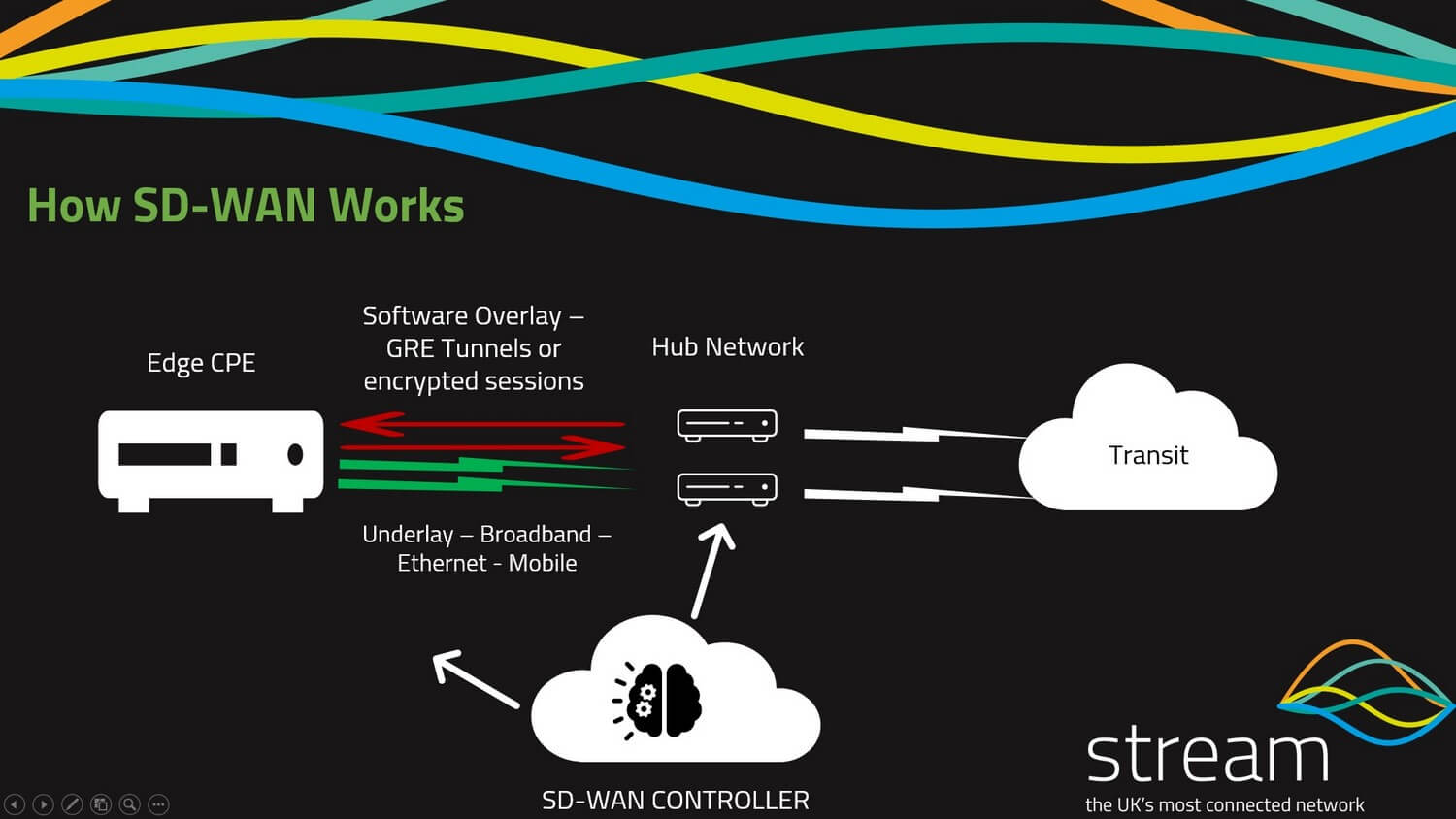
An SD-WAN edge or endpoint is a device or router that connects your local area network to the software-defined WAN. Consider it as your SD-WAN terminating device which connects your underlay (Ethernet, 4G LTE, MPLS circuits, Broadband) connectivity to the SD-WAN network.
Key Points to consider with SD-WAN Network Edge / Endpoint devices
The first thing to consider when deploying SD-WAN edge devices is how many underlay circuits are you going to connect to your on-premises device and how much SD-WAN traffic do you want the endpoint to handle?
If for example, you want 4 underlay circuits, you will need to ensure the device you connect has enough WAN interfaces to support the 4 circuits and you need to check how your underlay terminates be it broadband or ethernet to ensure it supports the network termination interface.
You also need to check how much SD-WAN traffic you are planning to use at each location as this will have an implication on the device used. With all SD-WAN vendors, each edge device will have a maximum throughput limit so the higher the network traffic the bigger and more expensive the device required will be.
Your SD-WAN managed service provider should work with you on the network design and understand the traffic requirements across your whole network to ensure scalability.
Another key point to consider when choosing your SD-WAN provider and edge device is to understand the capabilities of the solution. Some SD-WAN vendors do not support Next-Generation Firewall technology and deliver Virtual Network Functionality (VNFS) only. In this case, you will need additional Firewalls to sit behind your SD-WAN network to provide security.
Ideally, your SD-WAN solution should support both Next-Gen Security as well as VNFS.
What is SD-WAN Underlay?
SD-WAN underlay is the way you connect to the network, be it standard Internet connections using fibre broadband, mobile, ethernet or an existing MPLS network.
Key Points to consider with SD-WAN Underlay
To get the most out of an SD-WAN deployment you should have a minimum of two underlay circuits otherwise you won’t get the full benefits of application steering. If you only have one local internet connection, you won’t benefit from SD-WAN’s ability to steer applications to a better local path which is one of the major selling points of an SD-WAN network.
SD-WAN promises to reduce overall network costs as you can pick and choose the connectivity at each site, using lower-cost broadband circuits. But is important to do your research and evaluate your existing network provision – it may not always be cheaper to have two or more circuits at one site.
What is Application Performance Monitoring?
Application Performance Monitoring is a key SD-WAN technology providing, network segmentation and resiliency for individual app traffic and network services. As more enterprises consume public cloud (Azure, AWS, Google Cloud), software as a service applications such as Salesforce and with IT infrastructure being delivered by cloud providers the need to ensure your users have a quality of experience when using cloud applications is important to business productivity.
Application Performance Monitoring is normally delivered using a protocol such as AppQoE (Application Quality of Experience). APP QoE in conjunction with protocols APP ID and APBR (Advanced Policy Based Routing) identifies individual application traffic flows across a network and based on the SLA set for minimum jitter, latency, packet loss and bandwidth utilization on an underlay circuit, AppQoE will automatically look for a better path on the network if any of the metrics are broken.
For example, we could say for any Microsoft RDP traffic to have a minimum latency of 15ms and packet loss less than 1% and if this SLA is broken to find a better path on the network. Application Performance Monitoring delivers a quality of experience and automation of traffic flows across a network.
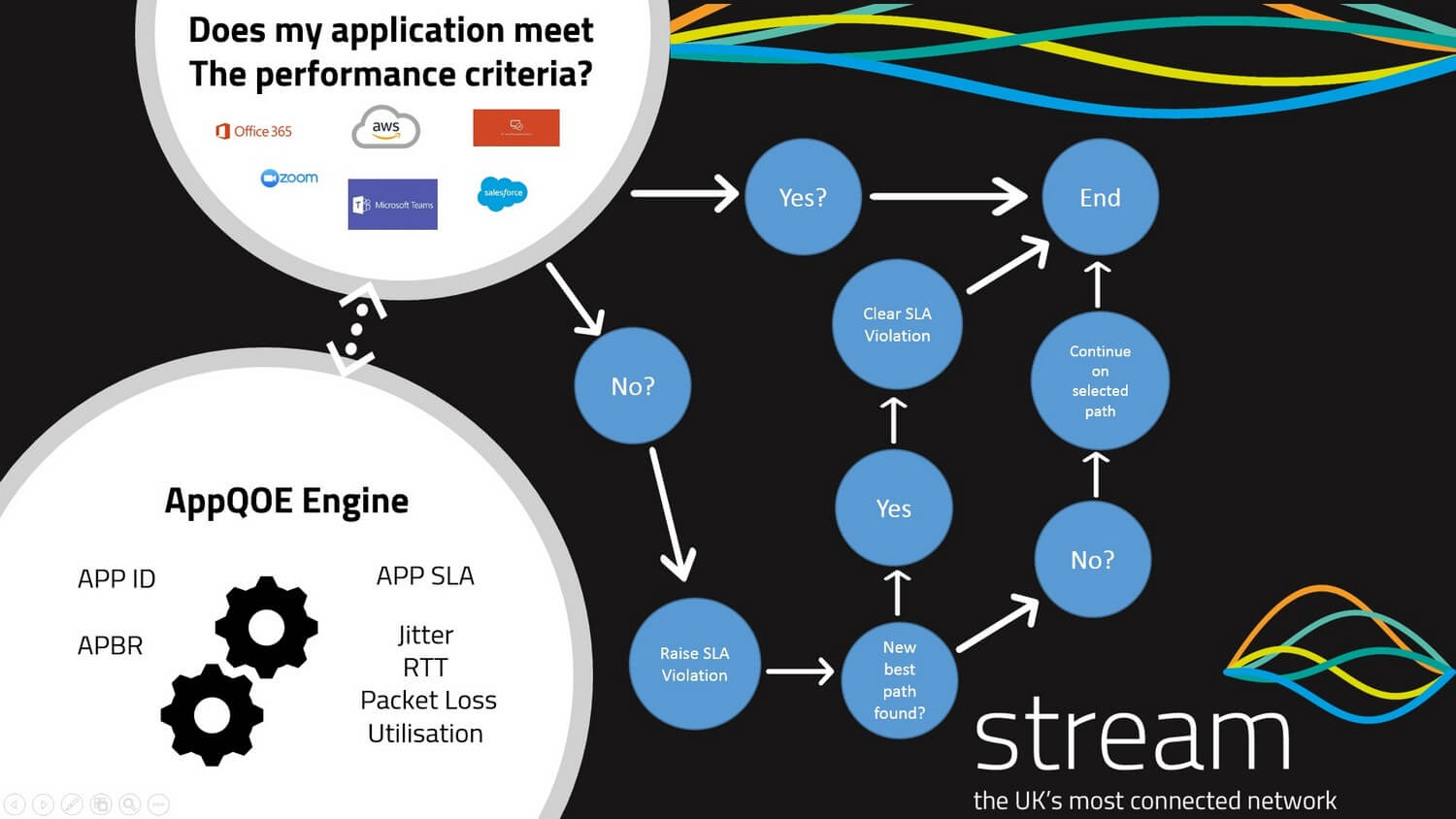
Key Points to consider with Application Performance Monitoring
The single most important issue to consider is that to benefit from application performance monitoring you do need a minimum of two underlay circuits. It is not uncommon for an enterprise with a traditional WAN to only have one underlay circuit at a branch office and adding an additional circuit can increase the costs for deployment depending on the requirements at each site.
The other thing to consider is to identify the key applications that your business relies on and what the minimum packet loss, latency and Jitter is required to ensure the application performs across the network. Your SD-WAN provider should work closely with you to identify these key applications and demonstrate that the solution can deliver the performance required.
SD-WAN Architecture Summary
SD-WAN offers many benefits for the modern cloud-enabled enterprise, from orchestration and automation of your network to security and scalability.
If you are considering deploying SD-WAN, ensure you cover the bases and you have the right SD-WAN architecture to meet your business needs now, but which can scale effectively in the future. Consider the cost implications of deploying SD-WAN and what key features you need both in network design, security, and application management. Find out more about Stream Networks SD-WAN services here.
If you would like further help and advice on SD-WAN, please contact one of our specialists on 01635 884170 or fill out the contact form below.

